Last week I wrote about interesting physics that can be done with ultracold atoms. One of the experiments I described was related to the Hanbury Brown-Twiss effect. Although I mentioned the experiment in some detail, the focus of my post was more on the analogies between ultracold atom systems and other physical systems. I did only briefly mention the wider impact of the original Hanbury Brown-Twiss experiment on our understanding of the particle-wave duality of light.
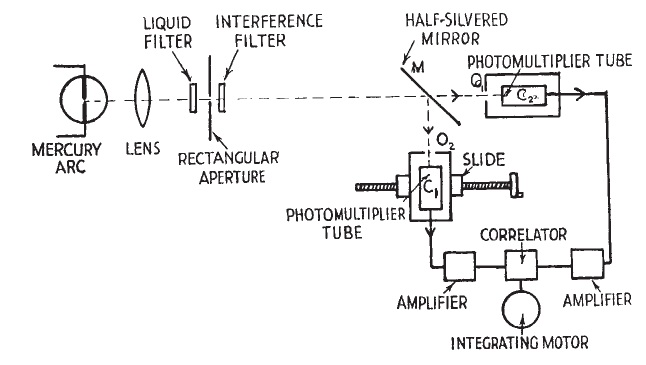
The Hanbury Brown and Twiss experimental apparatus from their 1956 Nature paper. (c) 1956 Nature Publishing Group.
As Chad Orzel mentioned in detail, a version of the experiments by Robert Hanbury Brown and Richard Twiss is a key contribution to the debate on the nature of light and represents an unambiguous proof that photons do exist.
He has now written more on how the experiment on atom lasers that I wrote about fits into this context. The description of Hanbury Brown and Twiss effects in ultracold atom systems is very lucid and provides a wonderful introduction to the experiments not only on ultracold atoms but also on photons.
The Hanbury Brown and Twiss experiment is one of the milestones in physics, and influenced the work by Roy Glauber on the quantum theory of optical coherence that got him half of the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Reference:
BROWN, R., & TWISS, R. (1956). Correlation between Photons in two Coherent Beams of Light Nature, 177 (4497), 27-29 DOI: 10.1038/177027a0


August 25, 2010
Comments Off on More Hanbury Brown and Twiss fun